When I was learning to read Linux source code, I used Cscope with Vim. But over time I felt it lacked crucial functionality, such as documentation lookup. The most frustrating thing is when I want to see the implementation of spinlocks, it gives me all the implementations from all architectures under all configurations, which is super overwhelming.
Recently, I met Neovim and fell in love with its plugin ecosystem, especially its LSP support. I've tried basepyright (Python) and rust-analyzer and want to try Clangd, an LSP for C.
The configuration for Linux is not as simple as for Python and Rust projects. Though I referenced online resources, it took quite a lot of time for me to get it to work. Hope this tutorial works for you.
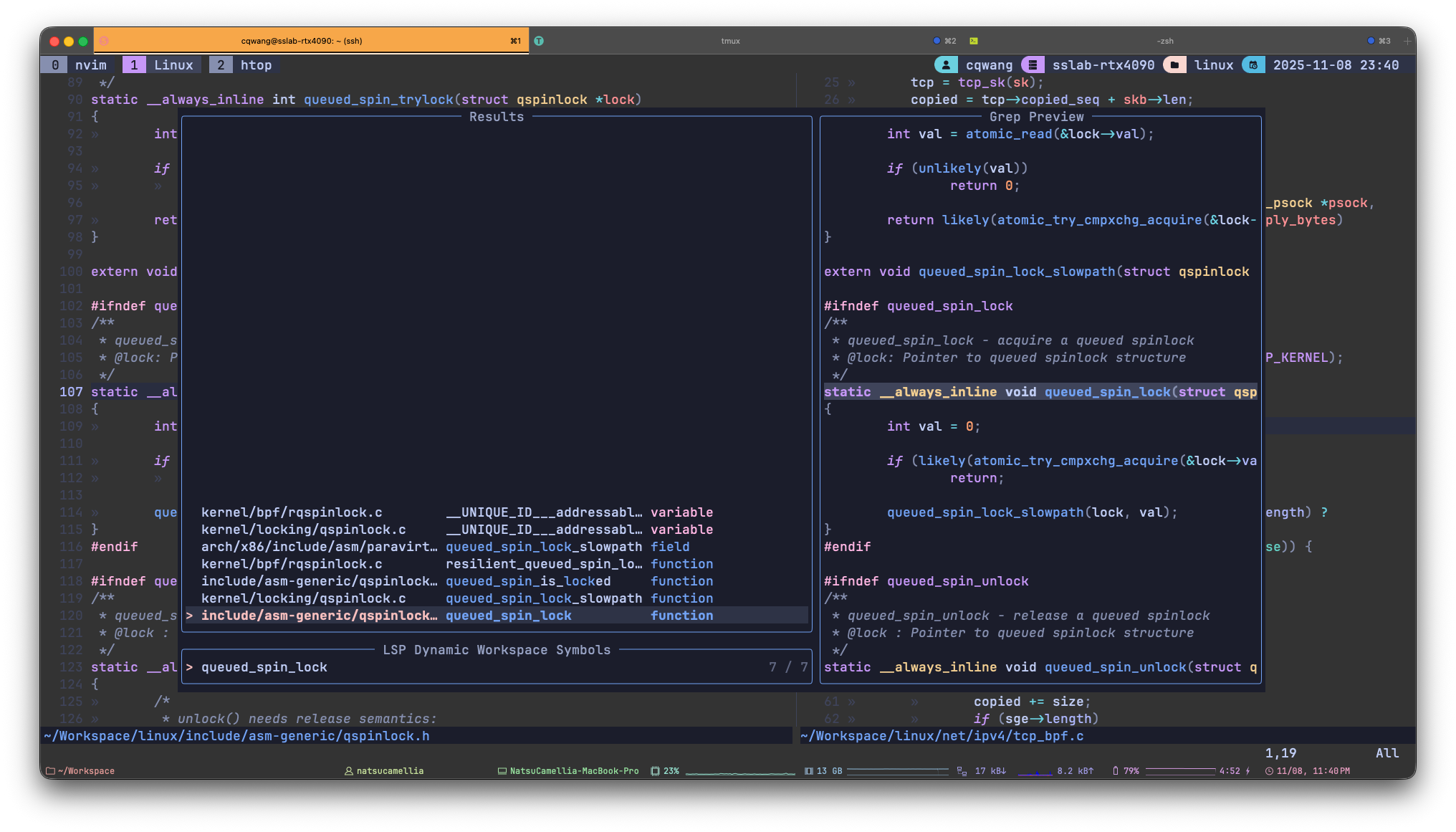 Lookup
Lookup queued_spin_lock with Clangd in Neovim
Generate compile_commands.json for Clangd¶
Clangd needs compile_commands.json to know where to find headers and which headers to use, especially when you want to search for arch-specific implementations such as spinlocks and memory barriers.
I want to set up Clangd for arm64 code with default Clang, so I ran the command to generate compile_commands.json under Linux's root directory:
yes "" | make ARCH=arm64 LLVM=1 compile_commands.json -j24Here's what the arguments mean:
ARCH=arm64: I want to setup Clangd for arm64 code.ARCHis your machine architecture by default.LLVM=1: Forces Make to use Clang because some gcc flags confuse Clangd.-j24: Tells Make to compile Linux in parallel with 24 CPU cores.yes "": Accepts all default configurations.
Setup Clangd LSP in Neovim¶
I typically browse Linux source code with Neovim and its Clangd LSP. If you're new to Neovim and interested, I recommend you watch this fun tutorial by TJ DeVries.
Basically, we're going to add the Clangd LSP to the Neovim LSP framework. Then we can interact with Clangd via the standard Neovim LSP interface.
{
'neovim/nvim-lspconfig',
dependencies = {
{ 'mason-org/mason.nvim', opts = {} },
'mason-org/mason-lspconfig.nvim',
'saghen/blink.cmp',
},
config = function()
local capabilities = require('blink.cmp').get_lsp_capabilities()
local cpu_info = vim.loop.cpu_info()
local cpu_cores = #cpu_info
local servers = {
-- Other LSPs
clangd = {
cmd = {
"clangd",
"--header-insertion=never",
"-j=" .. cpu_cores,
"--completion-style=detailed",
"--function-arg-placeholders",
"--rename-file-limit=0",
"--background-index",
"--background-index-priority=normal",
},
filetypes = { "c", "cpp", "objc", "objcpp" },
},
}
-- Setup language servers
for server, opt in pairs(servers) do
opt.capabilities = vim.tbl_deep_extend('force', {}, capabilities, opt.capabilities or {})
vim.lsp.config(server, opt)
end
-- Install LSP with Mason
local ensure_installed = vim.tbl_keys(servers or {})
require('mason-lspconfig').setup {
ensure_installed = ensure_installed,
automatic_installation = true,
}
end
}I'm also new to Neovim and not familiar with the settings. So there might be something wrong in the config.
The Clangd command is from Linux Kernel Development for Neovim and the setup commands are from x56Jason/nvim. The usage of nvim-lspconfig has been changed since Neovim 0.11 and I've fixed the commands to fit the usage.
You can check my Neovim settings in my GitHub repo